Photobiomodulation Reduces Abdominal Adipose Tissue Inflammation in Diet-Induced Obese and Hyperglycemic Mice
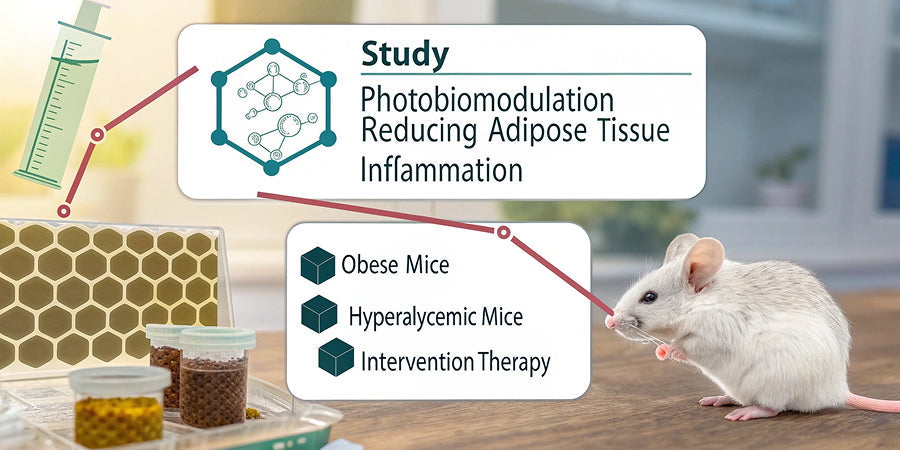
Study: Photobiomodulation Reduces Adipose Tissue Inflammation in Obese Mice
Study Overview
- Description: This study investigated whether photobiomodulation (PBM) could manage the chronic inflammatory component of obesity and hyperglycemia, given that systemic inflammation is closely related to insulin resistance and type-2 diabetes.
- Source: PubMed
Summary
- Participants: Obese and hyperglycemic mice.
- Intervention: Photobiomodulation (PBM) therapy. (Specific wavelength or duration details are not provided in the abstract snippet, but it implies a phototherapeutic approach.)
- Methods: The study evaluated the mice's body mass, glycemia, and the inflammatory infiltrate of their abdominal adipose tissue.
- Conclusion: Photobiomodulation (PBM) was found to reduce the abdominal adipose tissue inflammatory infiltrate in diet-induced obese and hyperglycemic mice, suggesting its beneficial effects on inflammatory disorders could extend to managing chronic inflammation associated with obesity and hyperglycemia.