1064nm-LLLT Induced Osteogenic Repair
Study Overview
- Description: This review aimed to analyze the literature on the effects of low-level laser therapy (LLLT) on bone repair processes and to discuss its mechanisms of action.
- Source: PubMed
Summary
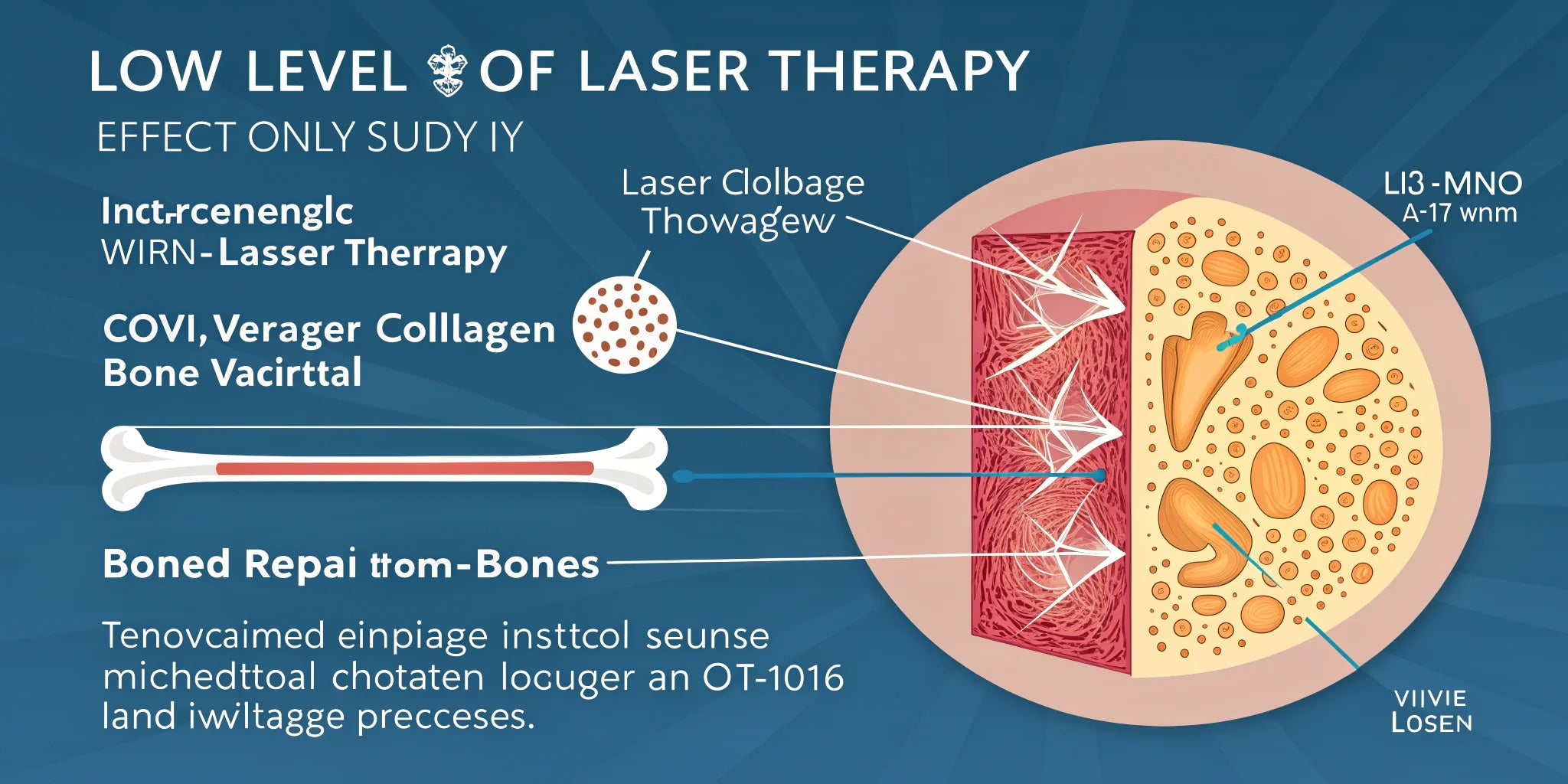
- Background Data: Laser therapy is considered an important tool for positively stimulating bone both in vivo and in vitro.
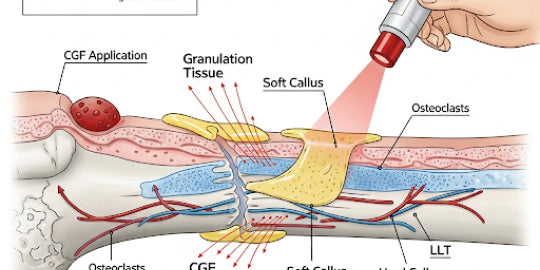
- Findings: Bone irradiated with infrared (IR) wavelengths showed increased osteoblastic proliferation, collagen deposition, and new bone formation. This effect was more effective during early stages of treatment when high cellular proliferation occurs. Vascular responses to laser therapy were also suggested as one of the possible mechanisms for the observed positive clinical results.
- Conclusion: The effect of laser therapy on bone regeneration may depend not only on the total irradiation dose but also on the irradiation time and mode. The energy density and intensity are biologically independent parameters, which accounts for the success and failure of laser therapy achieved at low-energy density levels.